Online dating market overview: how much dating applications earn and what are their business models. Part 2

Today, we’ll continue with the online dating market overview. In the second part, we’ll learn about the target audience of dating sites/apps. how they earn money, trends, and prospects of the dating market and, finally.
Target audience of the dating services
In 2017, ‘Kaspersky Lab’ and research company ‘B2B International’ had conducted a survey among 6458 online dating users from 30 countries and compiled an average portrait of a person who searches a date through the Internet.
Such a person is most likely to be a 33.8-year-old, male and full-time worker (63%). Otherwise, it’s a middle manager (20%) or a highly qualified specialist – a scientist, teacher or engineer (19%). Heads of companies and business owners make up 11% of online dating users.
In the course of their research, ‘Kaspersky Lab’ and ‘B2B International’ have found that finding a partner is not the most common goal among users:
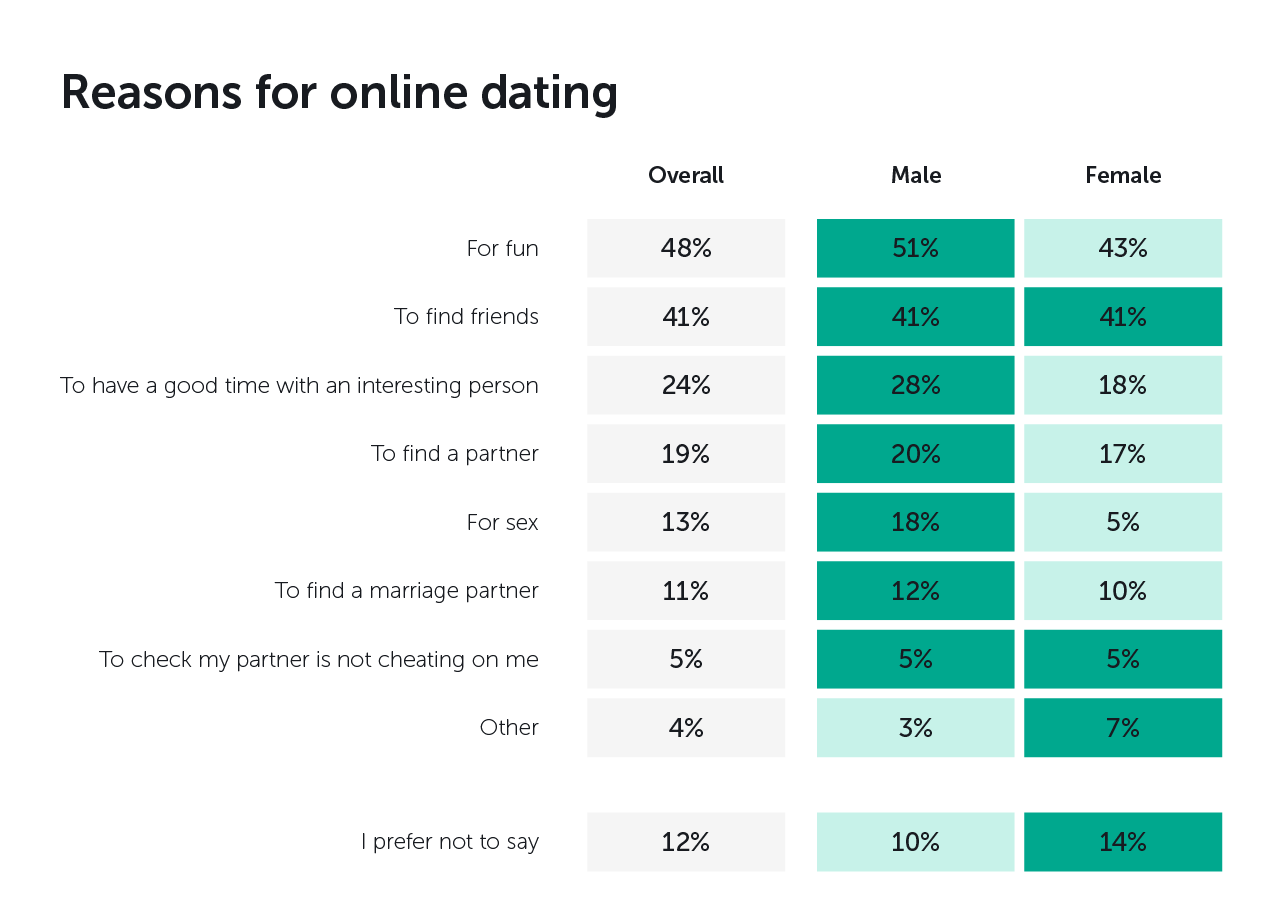
They also noticed that 57% of surveyed users lie about themselves, most of them (67%) were married men.
Online dating statistics show that 20% of those who are now in a serious relationship, started them online. And according to the ‘Match Group’ 600 million single people have access to the Internet all over the world, and 400 million of them have never used the dating app.
The gender ratio on sites or in applications is usually not balanced. In general, according to Dating Sites Reviews, the audience consists of 40% women and 60% men: 52.4% of men and 47.6% of women are registered on eHarmony, while on Tinder – 62% of men and 38% of women. In Badoo, 55% are men and 45% are women.
The main age group is millennials. According to ‘Kaspersky Lab’ and ‘B2B International’ survey, 43% of users are between 25 and 34. According to Tinder statistics, half of their audience is from 18 to 24 years old, and 85% of their users are from 18 to 34 years old.
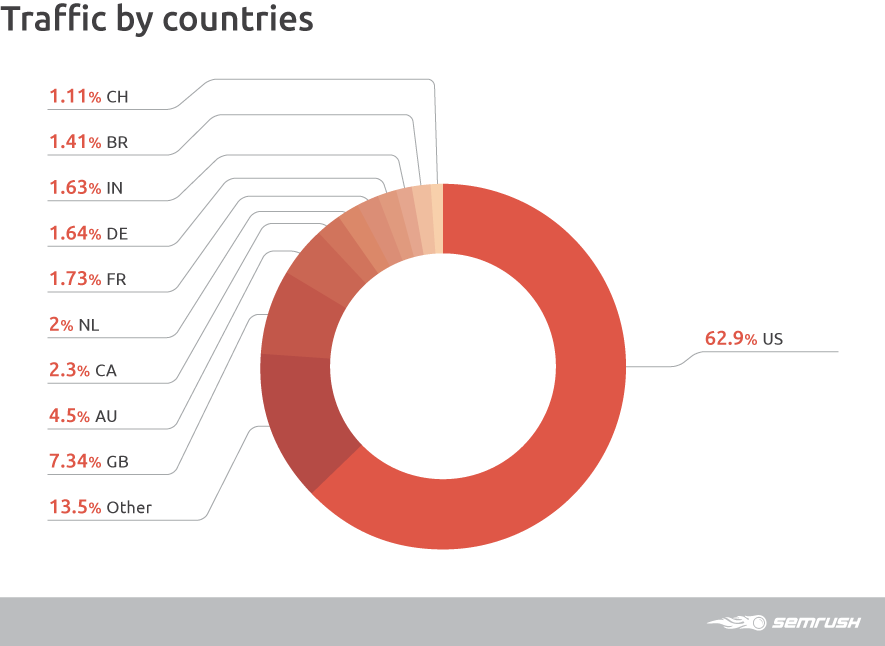
Geographically, a large part of the online dating sites traffic falls on the United States – 62.9% in total. The second place is occupied by the UK with 7.34% of traffic.
In general, English-speaking countries (USA, UK, Australia, and Canada) account for 77% of the global dating sites traffic.
How online dating services earn
The monetization in this area is divided into four main categories: paid subscription, freemium, advertising and premium accounts.
Paid subscription
The fee may be regular, monthly, or one-time, from today onwards.
The subscription fee system is implemented at the Match.com service, where access to the site for a month costs $40.
Some companies introduce subscription discounts for a one-time fee for longer periods. eHarmony costs $42.95 per month when you pay half a year, $25.95 per month for an annual subscription, and $10.95 per month for a two-year subscription.
One-time payments for the entire period of use are less common.
Freemium
Free use of the main features and additional options for a fee. Another option: earnings on ads in exchange for free use.
The main reason behind the freemium model is to spread information about the product and increase user loyalty.
Paid services are usually divided into two categories: the first is to promote your profile, the second is to expand the functionality of the system, also called ‘VIP’ groups or statuses.
Advertising
The owner of the app or site accepts ads from third parties, places them on its platform, and earns on clicks, views or transactions.
There are, for example, souvenir and gift shops banners or contextual ads, flower delivery services, plush toys or underwear, and etc, the possibilities of advertising are not limited to only these areas.
Premium model
Sometimes the basic features of the service are available only after joining the user club.
Investing in Dating
According to Joanna Glasner, a reporter for Crunchbase News, venture capital investors invested $ 127 million in 27 dating startups around the world in 2018.
Almost 80% of all investments in the dating sphere in 2018 went to a single company – the Chinese application for homosexual men called ‘Blued’, made in the Grindr-like style.
While in 2017, it was the Chinese mobile dating app Tantan that collected the biggest part of the investments, and in 2014, the Beijing dating site Baihe collected $ 250 million.
The Chinese market is very closed, it’s basically a separate Internet network. And it’s difficult for global dating services to enter it.
As a result, there is a field for growth as the audience is not yet spoiled. But the market is quickly globalizing, although there are still emerging new niches.
As a rule, dating services are presented in local markets, and project scaling is time-consuming and expensive. This is usually associated with increased marketing costs since there are quite a few competitors.
For beginners in the online-dating industry, it’s recommended to start with a niche and develop a product that will solve the “pain” of a particular audience – a particular age group or people with a common hobby.
Entrepreneur and investor Andrew Chen states that finding investments for dating startup is hard mostly because of the inevitable outflow of users and the high cost of attracting an audience, as well as:
- services are tied to the location;
- lack of balance between the number of men and women;
- the presence of inadequate people;
- a paradox: the better the dating service works, the faster the audience leaves it, as it meets its pair;
- inverse dependence of age and money (the more solvent the audience is, the older it is and the higher the chance that it no longer needs a dating service);
- problems of viral growth: users of dating services rarely admit that they visit such sites, word of mouth in this market does not work as others.
Trends and prospects of the industry
Vanessa Tao, the author of the Hong Kong digital marketing blog, notes three trends in the online dating industry that the market is aiming for:
1. Gamification
Today, the availability of gaming and entertainment components in an application or dating site is crucial for users. The most obvious example is Tinder or Badoo with their “swiping” features. “Such interaction with the service is perceived as a game, without the stigma of marriage service,” says Vanessa Tao.
2. Differentiation
“Niche services for dating today are rapidly conquering the market, and if the site owners cannot offer the users something unusual, unique, they leave. While Tinder attracts a mass market, Bumble, Grindr, and Happn are prime examples of positioning and segmentation of dating applications, ”writes Tao.
Not all market players share this position, some do not believe in the economic success of narrowly segmented startups.
3. Simplification
Even when it comes to finding a partner for a serious relationship, users are always looking for a simple, intuitive and user-friendly interface in the dating application.
One of the reasons for the success of Tinder is that users can simply import their Facebook profile into the app, without having to fill out those long questionnaires. Integration with social networks helped Tinder to attract the critical mass needed for its work.
Transition to the mobile market
Another important trend in the online dating industry is the transition of the audience to mobile platforms.
The online dating market has become 80% mobile.
Here the main trend is to solve the user’s problem as quickly as possible. In this case, those services that catch global trends win. For example – users actively use stories on Instagram — streams immediately appear in many dating services.
Judging by the trends in the US market, it can be said that the line between online dating and social networks will continue to blur. Facebook is testing its Secret Crush Dating, in Tinder users leave links to instant messengers and social networks.
Another trend – online dating is becoming safer, more transparent and predictable.